Today, I have two assignment following two reporters at the Star publication for a feature story related to dog breeding and a review of a night club in KLCC. Below are some photos from me today. More infor will upload soon. Cheers,
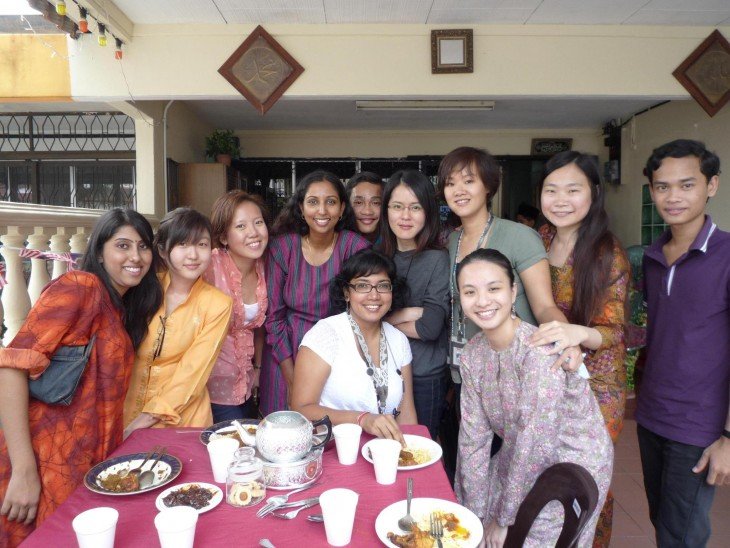
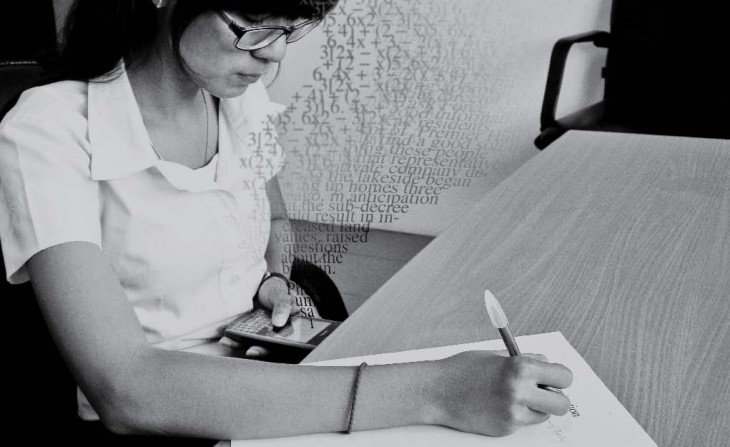
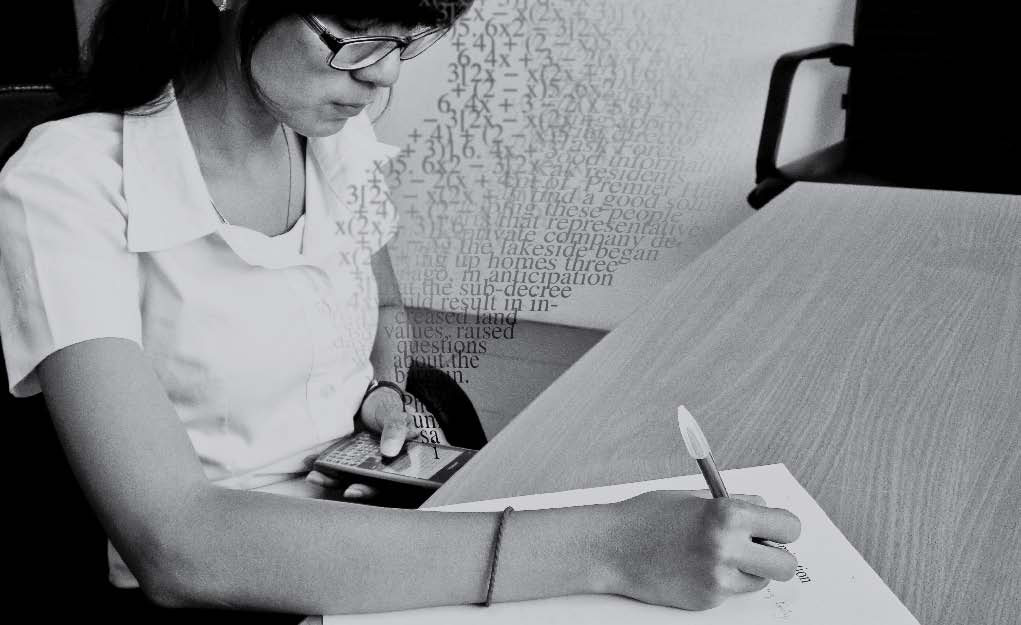
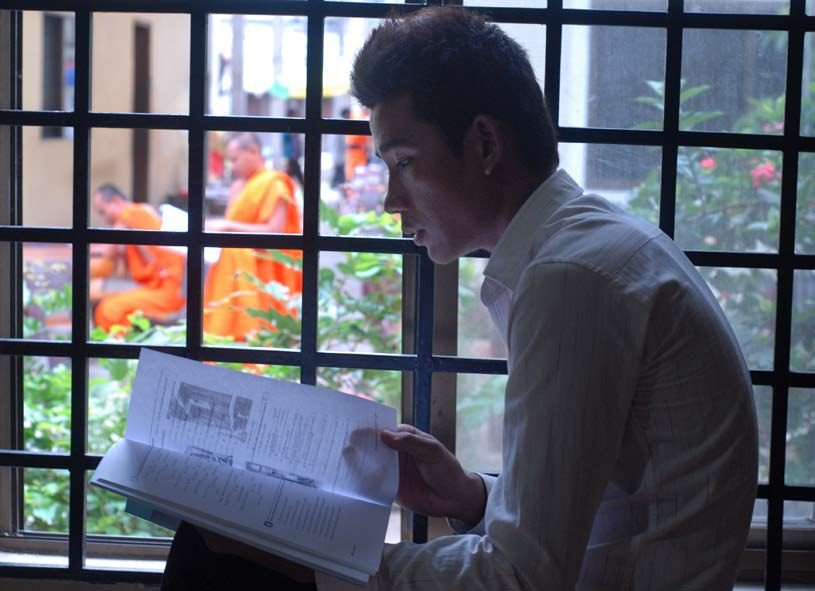
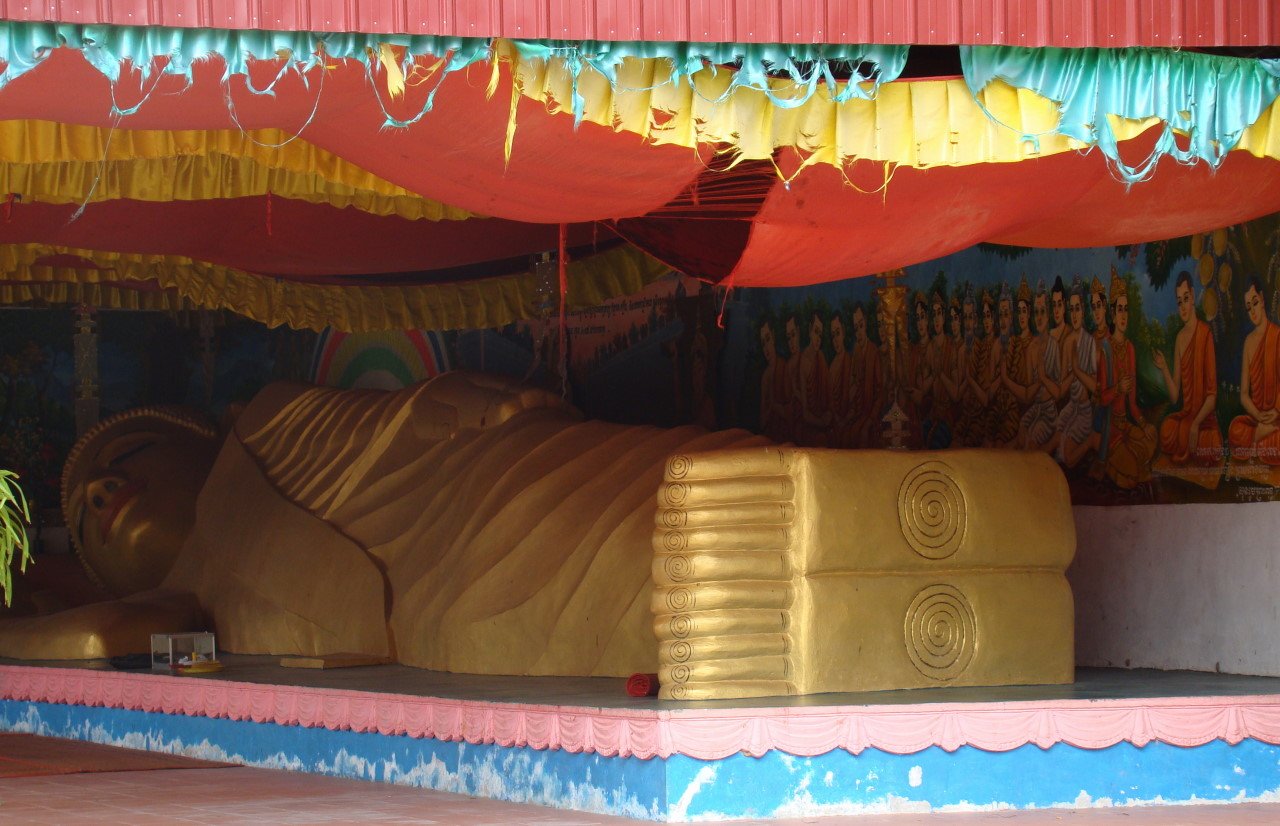
I went to sleep so late last night at 5am, so I got up super late at 12pm. Arriving the office at 3pm, I felt a bit shocked at first seeing not many people in the whole building and most of the light turned off because today is the public holiday, Independent day. There were only two people in my working place, metro section, a reporter I have to follow for my first assignment and another reporter. I left the office at 4pm with her to my interviewee house. He is a man who has a lot of experiences in breeding dogs, especially a dog from German. You can see some photos from the interview below:
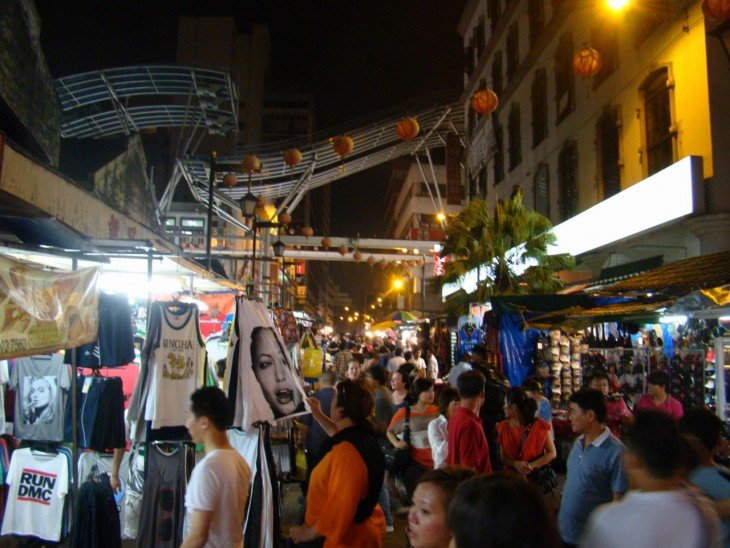
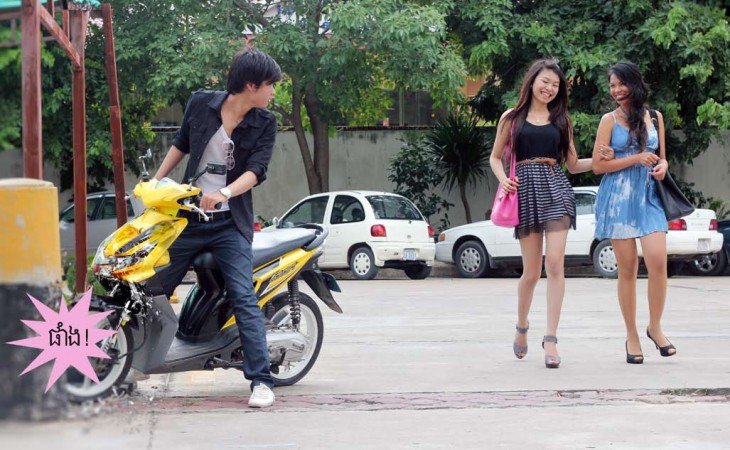
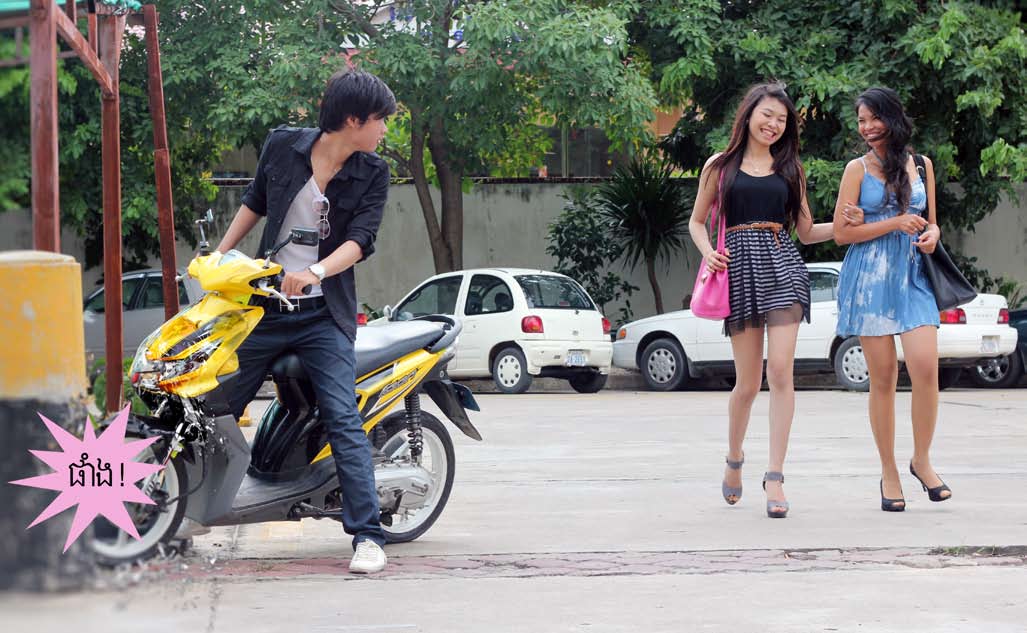
[slideshow]Then, I back to the office with her and arrived there at 7pm. Now, there is one more person in the room. She is the reporter I have to follow for another assignment today. We left the office immediately and there were four people now: my friend from Cambodia, two reporters, and me. She brought us to China Town first to have dinner. After having dinner, we walked around buying some staffs for about 2 hours before we left for the club we have to do a review for our newspaper. You can see some photos below when I was in China Town.
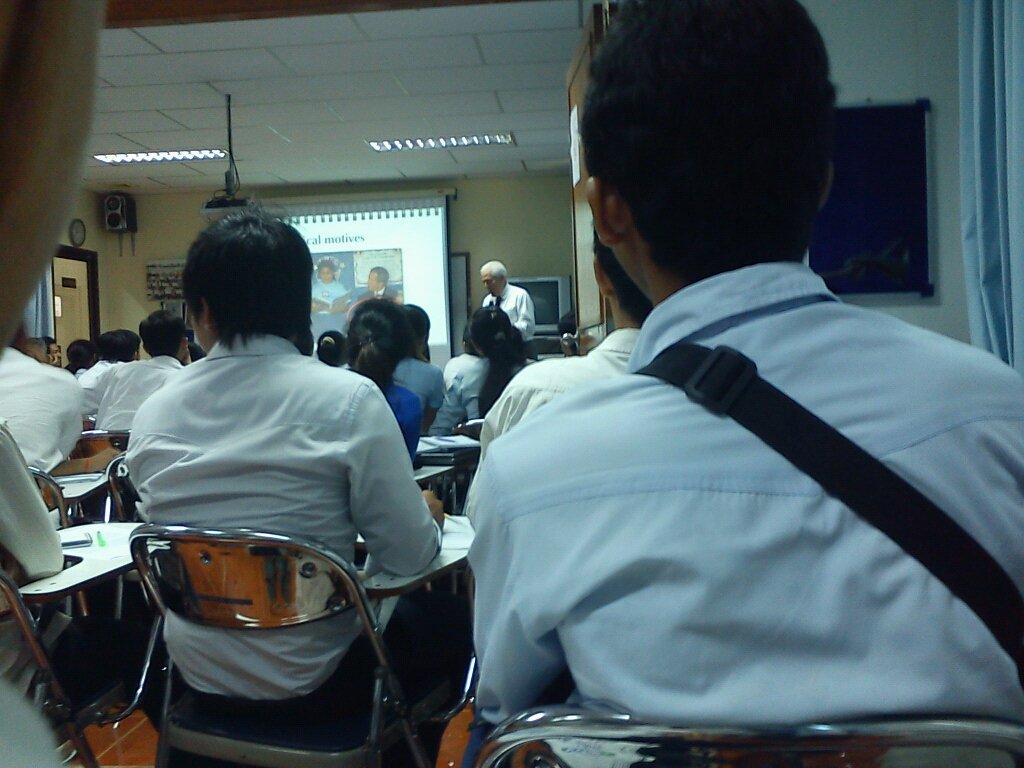
We arrived at the club at around 10pm seeing the manager there, interviewing him, and going around. There was another person in the team. He’s our photographer for this story. We all chitchatted until 11pm because the performing time started from 11pm to 3am. We all went inside the performance and dancing room and quite enjoyed there. I’ve taken some video which you can find it below.
[youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=drneI2AbUnY]I can say that I have a lot of fun today and really enjoy today assignments. My supervisor told me yesterday when he assigned me to follow the reporters that he wanted me to understand how nightlight in Malaysia is. I really like my supervisor because he cares for us as an interns.
I think it should be time for me to go to sleep because it’s late already. I have to finish writing these two articles as soon as possible and hand it in to the writers I followed to help checking information and editing before they were sent to the editor. Good night everyone and see you again soon.
31/08/2011
By: Dara Saoyuth